The word stomach is derived from the Latin stomachus which is derived from the Greek word stomachos, ultimately from stoma (στόμα), "mouth". The words gastro- and gastric (meaning related to the stomach) are both derived from the Greek word gaster
Anatomy of the Stomach
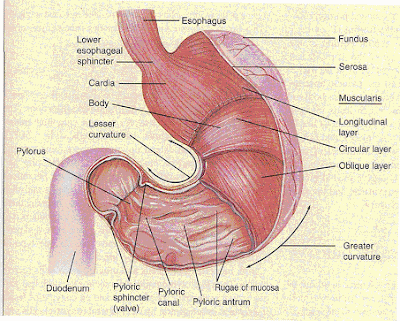
The stomach lies between the esophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is on the left upper part of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies against the diaphragm. Lying behind the stomach is the pancreas. The greater omentum hangs down from the greater curvature.Two sphincters, keep the contents of the stomach contained. They are the esophageal sphincter (found in the cardiac region, not an anatomical sphincter) dividing the tract above, and the Pyloric sphincter dividing the stomach from the small intestine.
The stomach is surrounded by parasympathetic (stimulant) and orthosympathetic (inhibitor) plexuses (networks of blood vessels and nerves in the anterior gastric, posterior, superior and inferior, celiac and myenteric), which regulate both the secretions activity and the motor (motion) activity of its muscles.
In humans, the stomach has a relaxed, near empty volume of about 45 ml. It is a distensible organ. It normally expands to hold about 1 litre of food,[4] but will hold as much as 2-3 litres (whereas a newborn baby will only be able to retain 30ml).
No comments:
Post a Comment